When embarking on a quest for enhanced well-being and vitality, many find themselves at a crossroads between two powerful allies in the world of supplements: ubiquinol and its precursor, ubiquinone. Both integral to the body's cellular energy production and revered for their antioxidant prowess, these two forms of CoQ10 serve as vital cogs in the machinery of our health. But why is ubiquinol better than CoQ10? A closer look at the science behind these compounds reveals a fascinating distinction that could significantly influence your supplement choices. Ubiquinol, often hailed as the superior form, boasts a unique advantage in its bioavailability. This trait makes it not just a supplement but a potent tool for those aiming for optimal health outcomes. This article delves into the heart of this distinction, exploring why ubiquinol, the reduced and active form of CoQ10 found naturally within the human body, emerges as the preferable choice for many.
Three compelling takeaways guide the journey toward understanding this preference. First, the enhanced bioavailability of ubiquinol, thanks to cutting-edge encapsulation technology and absorption enhancers, ensures it is more readily absorbed and utilized by the body—translating to immediate and impactful health benefits. Additionally, ubiquinol's role as a formidable antioxidant extends beyond mere protection against unstable molecules; it is instrumental in supporting heart health and potentially mitigating risks associated with blood pressure and congestive heart failure. Finally, the significance of ubiquinol in fostering fertility is undeniable, with clinical trials underscoring its ability to improve both sperm and egg quality, making it an essential consideration for individuals over 40 or those undergoing statin therapy. So, we invite you to explore the nuances of ubiquinol's superiority. This journey illuminates the difference between its oxidized and reduced forms and positions ubiquinol as a pivotal component of a proactive health and supplement routine.
Key Takeaways
- Ubiquinol offers higher bioavailability than ubiquinone, as the body more readily absorbs it due to advancements in encapsulation technology and the inclusion of absorption enhancers.
- Besides being a potent antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress, ubiquinol also supports heart health, potentially reducing blood pressure and improving symptoms of congestive heart failure.
- Ubiquinol has been shown to enhance fertility outcomes for both men and women, improving sperm and egg quality. It is especially recommended for those over 40 or on statin therapy due to age-related decline in natural CoQ10 conversion.
Understanding the Two Forms of CoQ10: Ubiquinol and Ubiquinone
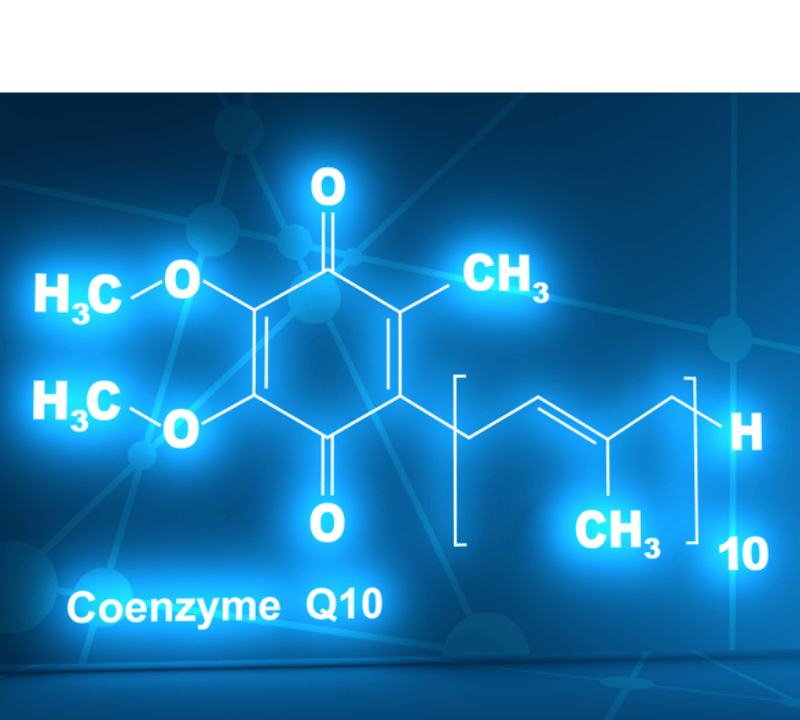
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is naturally present in the human body, mainly in ubiquinol and the ubiquinone form. Ubiquinol, the reduced form of CoQ10, is readily bioavailable for the body and is pivotal in cellular energy production. On the other hand, ubiquinone, the oxidized form, contributes significantly to ATP synthesis by acting as an electron acceptor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain.
Interestingly, our bodies balance these two forms through a constant conversion process, ensuring optimal functioning of the CoQ10 cycle and the maintenance of cellular energy production. CoQ10 supplements undergo the following conversion process:
- Initially, they are converted into ubiquinone in the small intestine upon ingestion.
- The ubiquinone is then absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Finally, it is transformed back into ubiquinol in the bloodstream.
This showcases the dynamic nature of CoQ10 bioconversion, which can be attributed to the presence of unstable molecules.
Despite initial thoughts, there is no substantial evidence to suggest that one form of CoQ10 is categorically superior to the other, as the body can efficiently convert ubiquinol and ubiquinone as needed.
Enhanced Bioavailability of Ubiquinol
Bioavailability, the proportion of a supplement that reaches systemic circulation and can be utilized by the body, is a key factor when considering dietary supplements. In the case of CoQ10, ubiquinol outshines ubiquinone in terms of bioavailability. Since ubiquinol requires no conversion, is immediately taken up, quickly absorbed, and efficiently transported in the blood, it is more easily absorbed by the body.
Recent advancements in encapsulation technology have significantly improved the bioavailability of ubiquinol supplements. Including absorption enhancers in ubiquinol supplements, such as oils or black pepper extract, has led to more efficient absorption, making this CoQ10 highly effective.
Soft Gel Capsules
Selecting the appropriate supplement form is vital when dealing with ubiquinol supplements. Research has demonstrated that soft gel capsules are indispensable in achieving maximum absorption of ubiquinol supplements.
Due to their ease of swallowing and enhanced absorption, softgels are generally preferred over other supplement forms.
The Antioxidant Advantage: Ubiquinol's Superiority
One of the reasons ubiquinol is gaining attention is its powerful antioxidant properties. The ubiquinol form:
- is the only known fat-soluble antioxidant naturally produced in the body
- defends cells from the accumulation of free radicals and oxidative stress
- neutralizes free radicals by reducing and neutralizing harmful compounds through their ability to exchange electrons between their redox forms.
In addition to its direct antioxidant activity, ubiquinol helps recycle other antioxidants like vitamins C and E, maintaining cellular redox balance. Unlike vitamin E, a chain-breaking antioxidant, ubiquinol prevents the initiation and propagation of lipid peroxidation in cell membranes and LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), playing a unique role in antioxidant defense.
Protection Against Oxidative Stress
The advantages of ubiquinol include:
- Its antioxidant activity
- Enhancing the cellular antioxidant network
- Scavenging free radicals
- Strengthening the body’s overall antioxidant defenses
- Directly reducing free radicals
- Aiding in the protection of cells from oxidative stress.
The prevention of lipid peroxidation by ubiquinol is significant for the integrity of cell membranes, safeguarding them from oxidative stress.
Supporting Heart Health with Ubiquinol

The heart, one of the most energy-demanding organs in the body, can benefit tremendously from ubiquinol. This form of CoQ10 boosts the efficiency of electron transport in the mitochondrial membrane, a critical factor in energy production in the heart. Research also suggests ubiquinol may help reduce blood pressure and improve symptoms of congestive heart failure.
Moreover, the supplementation of CoQ10, such as ubiquinol, has been associated with reducing oxidative stress markers in chronic heart diseases. Scientific studies portray ubiquinol as beneficial for promoting heart health and assisting in blood sugar regulation, thus making it a commendable choice for supporting cardiovascular health.
Cholesterol Management
In its quest to support heart health, ubiquinol may aid in managing cholesterol levels. It may lower LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol levels, contributing to better cholesterol management and cardiovascular health. Particularly for individuals with diabetes, who face a higher risk of heart disease, supplementation with CoQ10 forms like ubiquinol proves to be notably advantageous.
Boosting Fertility: How Ubiquinol Outshines Ubiquinone

The benefits of ubiquinol aren’t limited to heart health and antioxidant defense. It also plays a significant role in fertility. CoQ10 supplements, including ubiquinol, have enhanced both male and female fertility outcomes, particularly affecting egg and sperm quality. Daily ubiquinol supplementation at 200 mg has improved sperm density, motility, and morphology. The treatment duration positively correlates with seminal plasma antioxidant capacity and semen parameters.
Although current research on CoQ10’s impact on fertility is mainly based on ubiquinone, the superior absorption and bioavailability of ubiquinol suggest it could potentially be more effective. While more studies are needed for conclusive evidence, the current findings make ubiquinol a promising supplement for those aiming to improve fertility outcomes.
Female Fertility
For women, particularly those over 35, CoQ10 supplementation, including ubiquinol, may enhance egg quality, embryo quality, and pregnancy outcomes. These reproductive health benefits, combined with the potential for enhanced pregnancy outcomes, make ubiquinol a valuable supplement for women trying to conceive.
Male Fertility
For men, ubiquinol supplementation has led to significant improvements in sperm concentration, motility, and morphology, all of which are essential for successful conception. The use of CoQ10 supplements has been linked to an increase in seminal plasma total antioxidant capacity, suggesting a stronger defense against oxidative stress in the male reproductive system.
This direct impact of CoQ10 on sperm quality, including sperm motility, indicates a promising role in male fertility and sperm health.
Age-Related Decline in CoQ10 Conversion

As we advance in age, our body’s ability to efficiently produce and convert CoQ10 into its active form, ubiquinol, diminishes, usually around the age of 40. This decline in the enzymatic process required for converting conventional CoQ10 (ubiquinone) into ubiquinol can lead to a noticeable decrease in the CoQ10 levels that the body produces.
The decline in ubiquinol levels due to aging can lead to an increased risk of oxidative damage, which is tied to various degenerative diseases and aging processes. Ubiquinol dietary supplements are recommended for individuals over 40 and those on statin therapy to support heart health and combat statin-induced CoQ10 depletion.
Interactions and Precautions: What to Consider Before Choosing Ubiquinol
Despite the multitude of health benefits ubiquinol can offer, considering potential interactions and precautions is paramount. Ubiquinol may interact with blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and chemotherapy medications, which could lead to poor interactions. Moreover, statins, used to lower cholesterol, can reduce the body’s production of CoQ10, potentially necessitating supplementation with ubiquinol.
Before adding ubiquinol to your supplement routine, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for proper dosage assessment, as individual needs can vary. Individuals with the following conditions should also consult a healthcare provider before using ubiquinol:
- Liver or kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Hypoglycemia
- Breastfeeding
- Children and infants
Selecting the Right Ubiquinol Supplement
The selection of the appropriate ubiquinol supplement necessitates careful consideration. Opting for a formulation with the highest bioavailability to cater to individual needs is paramount. To ensure the quality and safety of ubiquinol supplements, look for products with third-party testing certifications from organizations like ConsumerLab.com, NSF, or USP.
A high-quality ubiquinol supplement should:
- Contain beneficial ingredients like vitamin E
- Avoid unnecessary additives, fillers, or potential allergens like soy
- Be free from animal-derived ingredients, such as gelatin, for vegan consumers.
The recommended daily dose of ubiquinol for most people starts between 100-200 mg, but individual requirements may vary based on health, age, and lifestyle.
Our comprehensive review article, "From Heart Health to Energy Boost: Finding the Best CoQ10 Supplement for You," can be valuable in selecting the perfect ubiquinol supplement. This review meticulously evaluates five of the top CoQ10 supplements available on Amazon, providing insights that could greatly inform your decision. Below is a link to this enlightening article designed to guide you toward making a choice that best supports your health and wellness goals.👇
Wrap-Up: Ubiquinol's Role in Optimal Health and Longevity
In wrapping up our exploration of ubiquinol, the reduced and active form of CoQ10, it's clear that its health-promoting prowess is undeniable. Ubiquinol stands out due to its enhanced bioavailability, which ensures that this fat-soluble antioxidant is more effectively absorbed by the body, making it a superior choice for supporting cellular energy production in almost every cell. Its potent antioxidant properties are instrumental in combating natural byproducts and environmental factors contributing to oxidative stress, thus safeguarding the body's cells. Furthermore, ubiquinol's ability to support heart health, demonstrated in placebo-controlled studies, highlights its potential in reducing blood pressure and improving symptoms of heart failure. Additionally, its significance in enhancing both male and female fertility, particularly in improving sperm motility and egg quality, cannot be overstated. This makes ubiquinol, especially in its supplemental form found in soft gel capsules, an invaluable addition to the supplement routines of those over 40 or individuals on statin therapy facing a natural decline in CoQ10 conversion.
When considering the integration of ubiquinol into your health regimen, it's crucial to account for potential interactions with medications and other supplements. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to tailor the dosage to your specific health needs, age, and lifestyle, ensuring you derive the maximum benefit from this powerful coenzyme. The selection of the right ubiquinol supplement, underscored by a commitment to quality and purity—free from unnecessary additives and aligned with dietary preferences—can significantly enhance your journey towards a healthier, more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who should avoid ubiquinol?
Ubiquinone may be safe for most adults when used as directed, but individuals with shallow blood pressure or certain medical conditions should avoid it. This includes those with diabetes, alcohol dependence, liver disease, and phenylketonuria (PKU).
Is ubiquinol the superior form of CoQ10?
There is no clear evidence that ubiquinol is a superior form of CoQ10 compared to ubiquinone, as the body naturally converts between the two forms, and the difference between them is unlikely to be significant.
What is the difference between ubiquinol and ubiquinone?
The main difference between ubiquinol and ubiquinone is that ubiquinol is the active, reduced form of CoQ10, while ubiquinone is the oxidized form that participates in ATP synthesis. Therefore, ubiquinol is more readily used by the body for energy production.
Why is ubiquinol considered more bioavailable than ubiquinone?
Ubiquinol is considered more bioavailable than ubiquinone because the body more readily absorbs it and does not require conversion, leading to immediate uptake and efficient transportation in the blood.
How does ubiquinol support heart health?
Ubiquinol supports heart health by enhancing energy production in the heart, reducing blood pressure, and improving symptoms of congestive heart failure. This makes it an essential component for maintaining heart health.
Thanks for exploring this simple question: "Why is Ubiquinol better than CoQ10?" Also, if you want to add to your library of knowledge, you should check out the other article mentioned and linked above. It never hurts to add to your knowledge arsenal!
Please return soon to check out our next review of another incredible supplement – we’re always looking out for YOU!
*We are NOT qualified medical advisors. The content here is only based on our personal opinions and should NOT be used as a substitute for a healthcare professional's advice!









Member discussion