In the vibrant world of nutritional science, a new star is rising: tocotrienols. These lesser-known vitamin E family cousins are stealing the spotlight with their extraordinary health benefits. If you thought vitamin E was all about tocopherols, prepare to be enlightened! With their unique chemical structure and potent antioxidant properties, Tocotrienols play a pivotal role in revolutionizing our understanding of dietary supplements. Their ability to seamlessly integrate into cell membranes and combat oxidative stress is a game changer for heart health and chronic disease prevention. In this article, we'll explore the best natural sources of tocotrienols and explore why they deserve a place in your wellness routine. Get ready to embark on an enlightening journey into the world of tocotrienols, where good health and science meet!
Key Takeaways:
- Tocotrienols, a lesser-known member of the vitamin E family, offer numerous health benefits, including cholesterol-lowering properties and protection against chronic diseases.
- The richest natural sources of tocotrienols include rice bran oil, palm oil, and annatto seed, each offering a unique composition of the different forms of vitamin E.
- Understanding the chemistry and antioxidant properties of tocotrienols can help individuals make informed choices about incorporating these potent antioxidants into their diets for a healthy cardiovascular system.
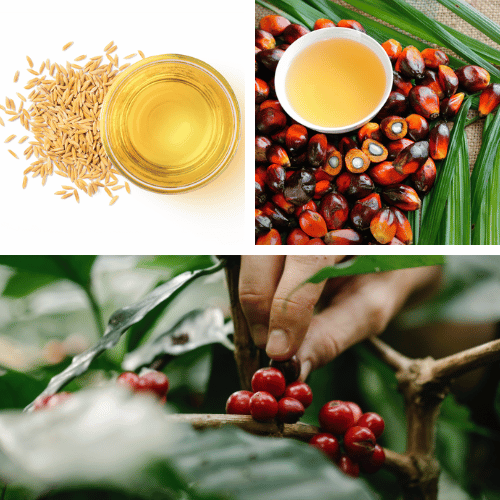

Rice Bran Oil: A Potent Source of Tocotrienols
Rice bran oil is often hailed as one of the best sources of tocotrienols. It is derived from the outer layer of rice grains and is a staple in many Asian cuisines. The oil boasts a balanced fatty acid composition. It is rich in gamma and delta tocotrienols, which have been linked to numerous health benefits, including lowering blood cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Palm Oil: The Versatile Provider of Tocotrienols
Palm oil, extracted from the fruit of the oil palm tree, is another significant source of tocotrienols. The oil is a common ingredient in both food and non-food products worldwide. Palm oil is particularly rich in alpha and gamma tocotrienols, which have been associated with protective effects against diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's.
Annatto Seed: The Richest Natural Source of Delta and Gamma Tocotrienols
Annatto seed, derived from the achiote tree, is a unique source of tocotrienols because it contains only tocotrienols, specifically delta and gamma forms, and is free of tocopherols. This makes annatto seed oil an excellent choice for those looking to maximize their intake of tocotrienols without the interference of tocopherols.
The Role of Tocotrienols in Cardiovascular Health
Tocotrienols have been extensively studied for their role in promoting a healthy cardiovascular system. Their cholesterol-lowering properties are particularly noteworthy, as they help maintain optimal blood cholesterol levels, a key factor in preventing heart diseases.
Tocotrienols and Their Impact on Chronic Diseases
Beyond cardiovascular health, tocotrienols have shown promise in preventing and managing various chronic diseases. Their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties make them valuable allies in the fight against conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Exploring the Spectrum of Vitamin E: Tocopherols and Tocotrienols
When discussing the best sources of tocotrienols, it's essential to understand the broader context of vitamin E. Vitamin E tocotrienols and tocopherols comprise this vital nutrient's eight forms. While alpha-tocopherol is the most common form of vitamin E in supplements, tocotrienols are gaining attention for their unique health benefits. Vegetable oils such as wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, and safflower oil are rich in various tocopherols, complementing the tocotrienols found in palm fruit, rice bran oil, and annatto seeds.
The interplay between tocopherols and tocotrienols is fascinating, as each has distinct bodily roles. Gamma-tocopherol, for instance, is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, while gamma-tocotrienol is recognized for its potent anticancer activity. These minor components of plant oils work synergistically to protect cell membranes from oxidative damage. The simultaneous determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in foods is crucial for understanding their combined effects on health, and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is often used for this purpose.
Tocotrienols: A Promising Ally in Cholesterol Management
Have you ever wondered how these mighty molecules work their magic on cholesterol levels? Tocotrienols, particularly the delta and gamma forms, are known for their cholesterol-lowering properties. They do this by inhibiting an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a pivotal role in cholesterol synthesis in the liver. This mechanism is similar to statins, the commonly prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs, but tocotrienols achieve this naturally.
Moreover, studies have shown that tocotrienols can reduce the LDL cholesterol (often called 'bad' cholesterol) and increase the HDL cholesterol ('good' cholesterol), a desirable balance for cardiovascular health. The delta-tocotrienols (d-tocotrienols), a specific form of tocotrienols, have been highlighted in research for their potent effects in managing cholesterol levels, making them a subject of interest for those looking to maintain a healthy heart through diet.
Also, the efficacy of tocotrienols in cholesterol management has been linked to their antioxidant capabilities and interaction with the cell membrane. Unlike tocopherols, tocotrienols exhibit a more uniform distribution within the lipid layers of the cell membrane, providing enhanced protection against lipid peroxidation and contributing to the maintenance of healthy blood vessels. This characteristic underscores the importance of including tocotrienol-rich foods or supplements in one's diet to potentially aid in preventing atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular diseases.
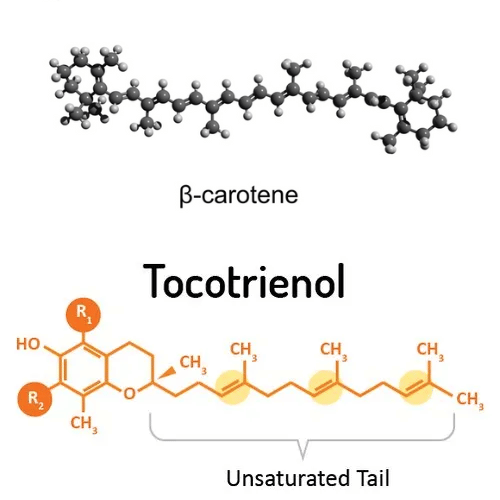
Tocotrienols and Beta-Carotene: A Dynamic Duo for Health
When discussing the best sources of tocotrienols, it's essential to consider their relationship with other nutrients, such as beta-carotene. Beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, is known for its immune-boosting and vision-supporting properties. Interestingly, some tocotrienol-rich foods, like palm oil, are also excellent sources of beta-carotene. This combination amplifies the antioxidant benefits, offering a more comprehensive approach to combating oxidative stress and supporting overall health.
Moreover, the synergy between tocotrienols and beta-carotene may enhance the cholesterol-lowering properties of tocotrienols. As both nutrients work together, they can provide a more robust defense against cardiovascular diseases. This makes a diet rich in tocotrienols and beta-carotene a strategic choice for those looking to improve their heart health and prevent chronic conditions.
Tocotrienols and Beta-Carotene: Partners in Antioxidant Defense
The synergistic relationship between tocotrienols and beta-carotene is a fascinating area of nutritional science. Beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, is renowned for its antioxidant capabilities, much like tocotrienols. When consumed together, they form a robust shield against oxidative stress, which is implicated in developing chronic diseases and aging. This partnership enhances the body's defense system, promoting cellular health and reducing the risk of oxidative damage.
Moreover, the combination of tocotrienols and beta-carotene has been shown to offer complementary benefits. While tocotrienols are particularly effective in protecting the lipid-rich areas of the body, beta-carotene excels in safeguarding fat-soluble regions. This dynamic duo works in tandem to ensure comprehensive antioxidant coverage, which is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing disease.
Tocotrienols and Beta-Carotene: Enhancing Cognitive Health
Beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, is often celebrated for maintaining good vision and skin health. However, combining beta-carotene with tocotrienols could be particularly beneficial for cognitive function. Studies suggest that the antioxidant properties of both compounds may work synergistically to protect brain cells from oxidative stress, contributing to cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer's disease. This dynamic duo may help preserve the delicate neural pathways essential for memory and cognitive function by neutralizing free radicals.
While alpha-tocopherol has traditionally been the focus of vitamin E research, tocotrienols are now emerging as a critical element in neuroprotection. Their unique chemical structure allows them to distribute across cell membranes more efficiently, potentially offering excellent protection against neurodegenerative processes. As research progresses, the combination of beta-carotene and tocotrienols could become a cornerstone in dietary strategies to maintain cognitive health well into old age.
Beta-Carotene: The Colorful Precursor to Vitamin A
When discussing beta-carotene, we're discussing more than just the pigment that gives carrots their vibrant orange hue. Beta-carotene is essential to maintaining healthy vision, skin, and immune function. But its benefits extend beyond these well-known functions. As an antioxidant, beta-carotene works with tocotrienols to combat oxidative stress, a critical factor in developing chronic diseases. This dynamic duo helps neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from damage and potentially slowing aging.
Moreover, the relationship between beta-carotene and tocotrienols doesn't stop at their antioxidant capabilities. Emerging research suggests that these nutrients may synergize when combined, enhancing each other's properties and offering a more robust defense against cellular damage. This is particularly relevant in the context of cardiovascular health, where oxidative stress can lead to the development of heart disease. By incorporating foods rich in both beta-carotene and tocotrienols, such as red palm oil or mixed nuts, individuals can harness the power of these nutrients to support overall well-being.
Beta-Carotene: A Visionary Nutrient in Alzheimer's Prevention
Beta-carotene is also emerging as a significant player in the realm of cognitive function. Studies suggest that this vibrant antioxidant may have a protective effect against cognitive decline, particularly in the context of Alzheimer's disease. The body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A, which is essential for brain health, potentially slowing the progression of Alzheimer's by safeguarding neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation.
Moreover, the synergistic relationship between beta-carotene and tocotrienols could offer a new frontier in Alzheimer's prevention strategies. While tocotrienols are known for their potent antioxidant properties, beta-carotene complements this by neutralizing free radicals that contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's. Together, they form a dynamic duo, working in concert to fortify the brain's defenses against age-related degenerative processes.
Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of Alpha-Tocopherol and Tocotrienols
As you may know, Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to memory loss and cognitive decline. While there is no cure for Alzheimer's, there is growing interest in the potential of certain nutrients to help protect brain health. Alpha-tocopherol, a form of vitamin E, has been studied for its neuroprotective properties. It is thought to slow the progression of Alzheimer's disease by reducing oxidative stress in the brain, which can contribute to neuronal damage. However, alpha-tocopherol doesn't work alone; it's part of a team that includes tocotrienols.
Alzheimer's disease is a complex condition with no single cause or cure. Still, the interplay between different forms of vitamin E, including alpha-tocopherol and tocotrienols, is gaining attention in the scientific community. A-tocopherol has long been recognized for its antioxidant capabilities. Still, tocotrienols are showing promise in their ability to modulate inflammatory pathways and amyloid plaque formation, both of which are hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. This suggests that a balanced intake of both forms of vitamin E could be more effective than either one alone in supporting brain health and potentially slowing the progression of Alzheimer's.
The challenge in Alzheimer's prevention is multifaceted, requiring a holistic approach to lifestyle and nutrition. Incorporating a diet rich in tocotrienols alongside adequate alpha-tocopherol levels may offer a protective effect against the onset of Alzheimer's disease. Foods such as annatto seeds, high in tocotrienols, and nuts and seeds containing alpha-tocopherol could be key components of such a preventative diet. As research continues to unfold, the nuanced relationship between these two forms of vitamin E could pave the way for new dietary recommendations to preserve cognitive health.
Delta Tocopherol: The Underappreciated Vitamin E
Though less studied than its tocotrienol counterparts, Delta-tocopherol holds significant potential in health and wellness. As a form of vitamin E, delta-tocopherol contributes to the body's antioxidant defense system, but it also has unique properties that set it apart. Its molecular structure allows it to interact with cell membranes differently, providing distinct benefits that are only beginning to be understood by the scientific community.
In the context of Alzheimer's disease, delta-tocopherol may play a crucial role. Emerging research suggests that this form of vitamin E could help mitigate the progression of neurodegenerative conditions. By protecting neurons from oxidative stress and modulating inflammatory responses, delta-tocopherol could be a key player in the fight against Alzheimer's and other forms of dementia, making it a subject of great interest for future clinical studies.
More About The Neuroprotective Effects of Tocotrienols in Alzheimer's Disease
As mentioned, tocotrienols may offer a ray of hope for those with Alzheimer's disease. The antioxidant properties of tocotrienols contribute to their neuroprotective effects, helping to combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which are key contributors to the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Research has indicated that tocotrienols can potentially slow down the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's by protecting neurons from damage.
The potential role of tocotrienols in neuroprotection, particularly in the context of Alzheimer's disease, is an area of growing interest. Alpha-tocotrienol, one of the eight parent compounds of vitamin E, has been studied for its neuroprotective effects. Research suggests that alpha-tocotrienol can mitigate the damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which are key factors in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. This protective action is considered superior to alpha-tocopherol, the most commonly known form of vitamin E.
In addition to their antioxidant action, tocotrienols have been observed to improve cerebral blood flow, which is crucial for maintaining cognitive function. This improvement in blood flow can help deliver essential nutrients and oxygen to brain cells, potentially mitigating some of the symptoms associated with Alzheimer's disease. Tocotrienols have also been observed to inhibit the formation of beta-amyloid plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. This inhibition is particularly associated with delta and gamma tocotrienols, which seem to have a more pronounced effect than beta-tocopherol and other forms of vitamin E. As research continues, tocotrienols may become a significant focus for developing dietary strategies and supplements to support cognitive health and prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
The Saponification Method: Unlocking Tocotrienols' Potential
The saponification method is a crucial process in extracting tocotrienols from various sources. This method involves treating vegetable oils with an alkali, which results in the hydrolysis of triglycerides and the release of free fatty acids and tocotrienols. This technique is particularly effective in isolating d-tocotrienols, among the most potent forms of vitamin E, in terms of their antioxidant capabilities.
By employing the saponification method, researchers and manufacturers can ensure a higher yield and purity of tocotrienols, making it easier to study their health benefits and incorporate them into supplements and fortified foods. This method is also instrumental in exploring the potential of tocotrienols in the prevention and management of Alzheimer's disease, as it allows for the precise extraction of these powerful compounds, which are believed to have neuroprotective effects.
The Extraction and Potency of Tocotrienols in Various Oils
Extracting tocotrienols from sources like palm oil and rice bran oil involves sophisticated techniques such as solvent extraction, saponification (mentioned above), and chromatographic analysis. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), particularly the normal phase variant, is commonly used to isolate these compounds. This allows for the precise identification and quantification of tocotrienols, ensuring that the richest source can be determined. For example, delta-tocotrienol, known for its cholesterol-lowering properties, is most abundant in annatto seeds.
On the other hand, oils like extra virgin olive oil, canola oil, and coconut oil contain varying levels of tocotrienols and tocopherols. These oils contribute to a balanced diet and offer different health benefits, such as the potential for cholesterol management and the prevention of chronic diseases like Alzheimer's. Extracting tocotrienols from these oils often involves saponification through alkaline digestion, which helps break down the oils and release the tocotrienols. Thin-layer chromatography can also analyze these components, although it is less precise than HPLC. The goal is to maximize the intake of tocotrienols vitamin, which is crucial for maintaining healthy adipose tissue and overall well-being.
Emerging Dietary Sources of Tocotrienols
While rice bran oil, palm oil, and annatto seed are the most well-known sources of tocotrienols, other emerging dietary sources include barley oil, oats oil, and certain types of nuts and grains. These whole foods contribute to a balanced diet rich in natural vitamin E forms.
The Extraction and Analysis of Tocotrienols
Methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography, thin-layer chromatography, and supercritical fluid extraction are employed to measure tocotrienol content in oils and foods accurately. These techniques ensure the precise identification and quantification of the different tocotrienol forms.
Tocotrienols in Clinical Research: Human Studies
Human studies on tocotrienols are crucial for understanding their impact on health. Research has shown that tocotrienol supplementation can lead to improvements in lipid profiles, reduction in oxidative stress markers, and potential benefits in managing medical conditions such as prostate cancer and Alzheimer's disease.
The Synergy of Tocotrienols with Other Antioxidants
Tocotrienols do not work in isolation. Their antioxidant activity is often enhanced with other antioxidants such as vitamin C, beta-carotene, and selenium. This synergy can lead to more potent health benefits and better protection against oxidative stress.
Tocotrienols vs. Tocopherols: Understanding the Differences
Both tocotrienols and tocopherols have their special place in the vitamin E family, but they're quite different in how they impact our health. Tocotrienols, for instance, are turning heads with their powerful antioxidant abilities, going beyond what tocopherols offer. They're linked to various health benefits, from lowering cholesterol to protecting our brains and even showing potential in cancer prevention.
If you're curious about the nitty-gritty of how these two types of vitamin E differ, you might find our previous article, 'Unveiling the Difference: How Do Tocotrienols Differ from Other Forms of Vitamin E?', really insightful. It digs deeper into what sets them apart and why we should pay attention to both in our diets. You can find the article here for a more detailed exploration.
The Future of Tocotrienols in Nutrition and Medicine
As we unravel the myriad health benefits of tocotrienols, their significance in nutrition and medicine is becoming increasingly evident. This exciting area of research is not just academic; it's paving the way for tocotrienols to become a key component in our daily health regimen. Imagine a future where tocotrienols are as common in our dietary supplements and functional foods as other well-known nutrients, all aimed at boosting our health and warding off diseases.
And if you're wondering about practical ways to incorporate tocotrienols into your routine, you're in luck! I've explored some of the best options in my article, 'Shattering the Vitamin E Stereotype: A Journey into the World of the Best Tocotrienol Supplements.' These top five supplements, sourced from natural annatto beans and palm oil extracts, represent the cream of the crop from reputable companies. They are not just supplements; they're a testament to how far research has brought us in understanding and utilizing tocotrienols. Curious to know which made the list and why? You can find all the details in the article by clicking on the link below. It's an exciting time for tocotrienols, and I can't wait to see where this journey takes us next!
Incorporating Tocotrienols into Your Diet
For those looking to increase their intake of tocotrienols, incorporating oils like rice bran oil and palm oil into their cooking is a simple way to start. Additionally, seeking out whole foods and supplements, like those listed in the article above, that contain these potent antioxidants can help ensure adequate consumption for optimal health benefits.
Tocotrienols: A Natural Solution for a Healthy Lifestyle
Tocotrienols offer a natural solution for individuals seeking to enhance their health and protect against disease. By choosing the right sources and understanding their unique properties, one can harness the power of these potent antioxidants for a healthier lifestyle.
Wrapping Up Our Discussion on Tocotrienols
Tocotrienols, a lesser-known but influential member of the vitamin E family, are emerging as key players in the field of health and nutrition. This comprehensive article delves into various aspects of tocotrienols, highlighting their unique properties and immense health benefits.
In summary, tocotrienols represent a significant advancement in our understanding of nutrition and health. Their unique chemical structure and potent antioxidant properties make them valuable additions to our diet. As research continues to reveal their diverse benefits, tocotrienols are set to transform the landscape of dietary supplements and functional foods, offering natural solutions for a healthier lifestyle. This article informs about tocotrienols' current standing in health and nutrition and paves the way for their promising future.
FAQ Section - Your Tocotrienol Questions, Answered!
We know that diving into the world of tocotrienols can spark many curiosity and questions. After all, understanding these lesser-known members of the vitamin E family and their myriad health benefits is fascinating and essential for making informed health choices. After reading our comprehensive article on tocotrienols, we've compiled this FAQ section to answer your questions.
We've got you covered, from their fundamental properties to their impact on health and how to incorporate them into your daily life. We aim to provide clear, concise answers to your most pressing queries, making your journey into the world of tocotrienols as enlightening and enjoyable as possible. So, whether you're a health enthusiast, a curious reader, or someone looking to optimize your diet, this FAQ section is for you!
1. What Exactly Are Tocotrienols and How Do They Differ from Tocopherols?
Answer: Tocotrienols are members of the vitamin E family, just like tocopherols, but with some critical differences in their chemical structure and functions. Both have a chromanol ring, but tocotrienols have an unsaturated side chain with three double bonds, whereas tocopherols have a saturated side chain. This structural difference makes tocotrienols more fluid and able to distribute more evenly in the cell membranes. This allows them to provide more effective antioxidant protection, particularly against lipid peroxidation in cell membranes. Tocotrienols are also thought to have unique biological activities, such as neuroprotective, cholesterol-lowering, anti-cancer, and anti-inflammatory properties, distinct from those of tocopherols.
2. How Do Tocotrienols Contribute to Heart Health and Cholesterol Management?
Answer: Tocotrienols contribute to heart health primarily by their ability to lower cholesterol levels. They are known to suppress the activity of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme responsible for cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Tocopherols do not share this action. Clinical studies have shown that tocotrienols can lower total cholesterol and LDL (bad cholesterol) levels while potentially raising HDL (good cholesterol) levels. Additionally, their antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the cardiovascular system, further promoting heart health.
3. Can Tocotrienols Help Prevent or Treat Chronic Diseases like Cancer?
Answer: Research suggests that tocotrienols have potential in the prevention and treatment of various chronic diseases, including certain types of cancer. They exhibit anti-cancer properties by promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancerous cells, inhibiting angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors), and hindering the spread of cancer cells. For example, studies have shown tocotrienols are effective against breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancer cells. However, it's important to note that while these findings are promising, more research and clinical trials are needed to understand their role in cancer treatment fully.
4. How Can I Incorporate Tocotrienols Into My Diet?
Answer: To increase your intake of tocotrienols, consider incorporating foods and oils rich in these compounds into your diet. Rice bran oil, palm oil, and annatto seeds are some of the richest natural sources. You can use rice bran or palm oil for cooking, and annatto seeds can be used as a spice or coloring agent. Specific whole foods like barley, oats, some nuts, and grains also contain tocotrienols. For a more concentrated source, tocotrienol supplements derived from these natural foods and oils are also available.
5. Are There Any Side Effects or Interactions I Should Be Aware of When Taking Tocotrienol Supplements?
Answer: Tocotrienol supplements are generally considered safe and well-tolerated. However, as with any supplement, there can be potential side effects or interactions with other medications. High doses of tocotrienols may increase the risk of bleeding, especially if taken with blood thinners like warfarin. They may also interact with cholesterol-lowering medications. It's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Thanks for taking this journey to explore the efficacy of this critical vitamin - Tocotrienol. And, if you want to add to your library of knowledge, you should check out the other articles mentioned and linked above. It never hurts to add to your arsenal!
Also, please return soon to check out our next review of another incredible supplement – we’re always looking out for YOU!
*We are not qualified medical advisors. The content here is only based on our personal opinions and should NOT be used as a substitute for a healthcare professional's advice!










Member discussion